Deep Vein Thrombosis: The Silent Killer You Need to Watch Out For
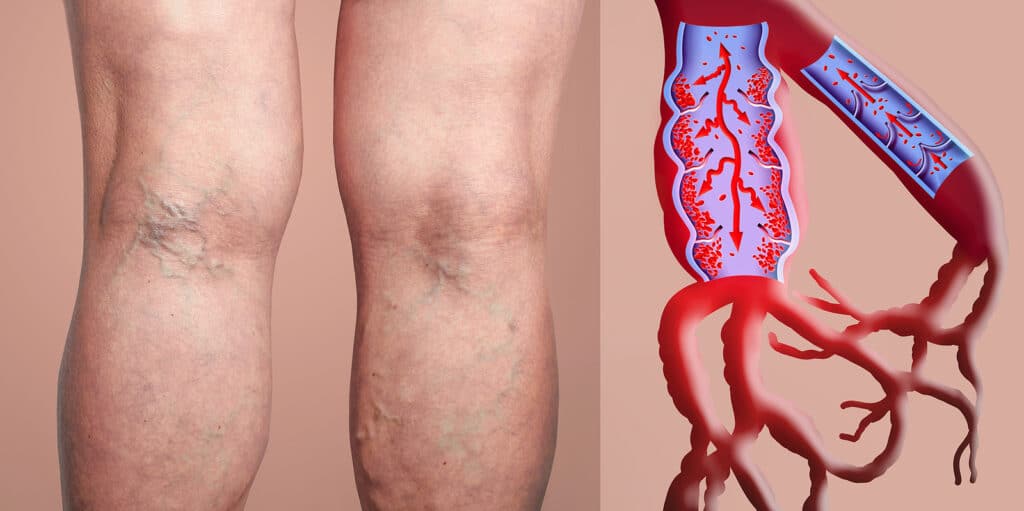
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in deep veins, predominantly in the legs. These clots can obstruct blood flow, leading to swelling, pain, and potential complications if the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE). Recent developments in medical research and notable cases have brought DVT into the spotlight, underscoring the importance of awareness, early detection, and treatment.
Recent High-Profile Case: Victor Wembanyama
In February 2025, Victor Wembanyama, a prominent 21-year-old center for the San Antonio Spurs, was diagnosed with DVT in his right shoulder. This diagnosis came shortly after his participation in the NBA All-Star game. The condition is expected to sideline him for the remainder of the season. The Spurs' medical team remains optimistic about his full recovery, noting that similar cases in the NBA have seen players return to peak performance post-treatment.
Understanding DVT
DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, often in the legs but sometimes in other parts of the body, such as the arms or shoulders. Factors contributing to DVT include prolonged immobility, injury to the vein, certain medical conditions, and, in some cases, genetic predispositions. Symptoms may encompass swelling, pain, redness, and warmth in the affected area. However, some individuals may remain asymptomatic until complications arise.
Innovations in Diagnosis and Treatment
Advancements in medical technology have enhanced the diagnosis and management of DVT. A notable development is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostic procedures. Researchers have explored AI-assisted compression ultrasound techniques, enabling non-expert healthcare providers to accurately identify DVT, thereby reducing the workload on specialists and expediting patient care.
In terms of treatment, mechanical thrombectomy devices have gained traction. These devices physically remove clots from the veins and have shown promise, especially in cases where traditional anticoagulation therapy is insufficient or contraindicated. For instance, Inari Medical's ClotTriever system received national reimbursement approval in Japan in December 2024, reflecting its growing acceptance in the medical community.
Environmental Factors and DVT Risk
Emerging research has identified environmental factors, such as air pollution, as potential contributors to DVT risk. A study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in December 2024 found that long-term exposure to air pollution is associated with an increased risk of blood clots in deep veins. The study highlighted that participants with greater exposure to fine particulate matter had a 39% increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes DVT and PE.
DVT in Specific Populations
Certain populations face a heightened risk of developing DVT. Pregnant women, for instance, are more susceptible due to physiological changes during pregnancy that affect blood flow and clotting mechanisms. In the UK, blood clots are a leading cause of death among pregnant women and new mothers, despite the overall mortality risk being low. Preventive measures, such as prophylactic anticoagulation, are essential during high-risk periods like hospitalization and pregnancy.
Preventive Measures and Awareness
Awareness and early intervention are crucial in managing DVT risk. Preventive strategies include:
-
Regular Movement: Especially during long periods of immobility, such as long-haul flights or bed rest, flexing and stretching the legs can promote blood circulation.
-
Hydration: Maintaining adequate fluid intake helps prevent blood from thickening.
-
Compression Stockings: Wearing these can aid in reducing the risk of clot formation by improving blood flow in the legs.
-
Medication: In high-risk individuals, healthcare providers may prescribe anticoagulants to prevent clot formation.
Recognizing the symptoms of DVT and seeking prompt medical attention can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. As medical research progresses, understanding the multifaceted nature of DVT—from environmental influences to technological advancements in treatment—remains essential for effective prevention and management.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/drugstore-retinol-creams-tout-f76b9d2796e34eaa8376801c83fb1888.jpg)











